Search Results for: point mutation
Point mutation
Definition noun, plural: point mutations (genetics) A small-scale mutation characterized by a change of only one nucleotide... Read More
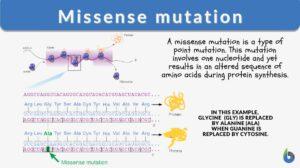
Missense mutation
What is a missense mutation? Literally speaking, a mutation that changes the meaning of the encoded gene sequence is the... Read More
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
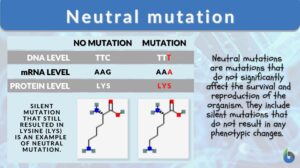
Neutral mutation
Neutral Mutation Definition What is a neutral mutation? Neutral mutations are the alterations in the DNA that are... Read More
Substitution mutation
Definition noun, plural: substitution mutations (genetics) A small-scale mutation characterized by a substitution of one or... Read More
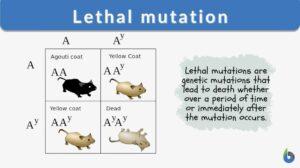
Lethal mutation
Lethal Mutation Definition Genetic mutations come from changes in the DNA structure or sequencing in an organism. Often... Read More
Small-scale mutation
Definition noun, plural: small-scale mutations (genetics) A type of mutation characterized by a change of one or few... Read More
Transversion
Definition noun, plural: transversions (genetics) A small-scale mutation characterized by the replacement of a purine by... Read More
Transition
Definition noun, plural: transitions (genetics) A small-scale mutation characterized by the replacement of a purine by... Read More
Genetic Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.Genetic Mutations Genetic mutations are inherited variations in an... Read More
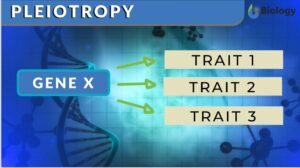
Pleiotropy
Pleiotropy Definition When one single gene starts affecting multiple traits of living organisms, this phenomenon is known... Read More
Nucleotide deletion
Definition noun A deletion of a single nucleotide causing a shift in the reading frame of the codons in the mRNA, thus, may... Read More
Base pair substitution
Definition noun, plural: base pair substitutions A type of mutation involving replacement or substitution of a single... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Transition mutation
transition mutation A point mutation involving substitution of one base-pair for another, i.e., replacement of one purine... Read More
Chromosomal inversion
Definition noun, plural: chromosomal inversions A chromosomal aberration wherein a segment of a chromosome is reversed... Read More
Sickle cell anaemia
Definition noun A hereditary blood disorder resulting in anaemia due to a mutation in the allele coding for the beta chain... Read More
Nucleobase
Definition noun plural: nucleobases (biochemistry) The base in the nucleic acid, e.g. purines and pyrimidines Details ... Read More
Pyrimidine
Definition noun plural: pyrimidines py·rim·i·dine, py·rim·i·dine A heterocyclic aromatic compound that presents as... Read More
Carrying capacity
Carrying Capacity Definition What is carrying capacity? In biology and environmental science, the carrying capacity of a... Read More
Axon hillock
Axon Hillock Definition What is axon hillock? If you are familiar with the different parts of the neuron, the axon hillock... Read More
Pericentric inversion
Definition noun, plural: pericentric inversions (genetics) An inversion of a segment of chromosome in which the centromere... Read More
Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory... Read More
Thymidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
Uridine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and three phosphate... Read More
Thymidine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and two... Read More